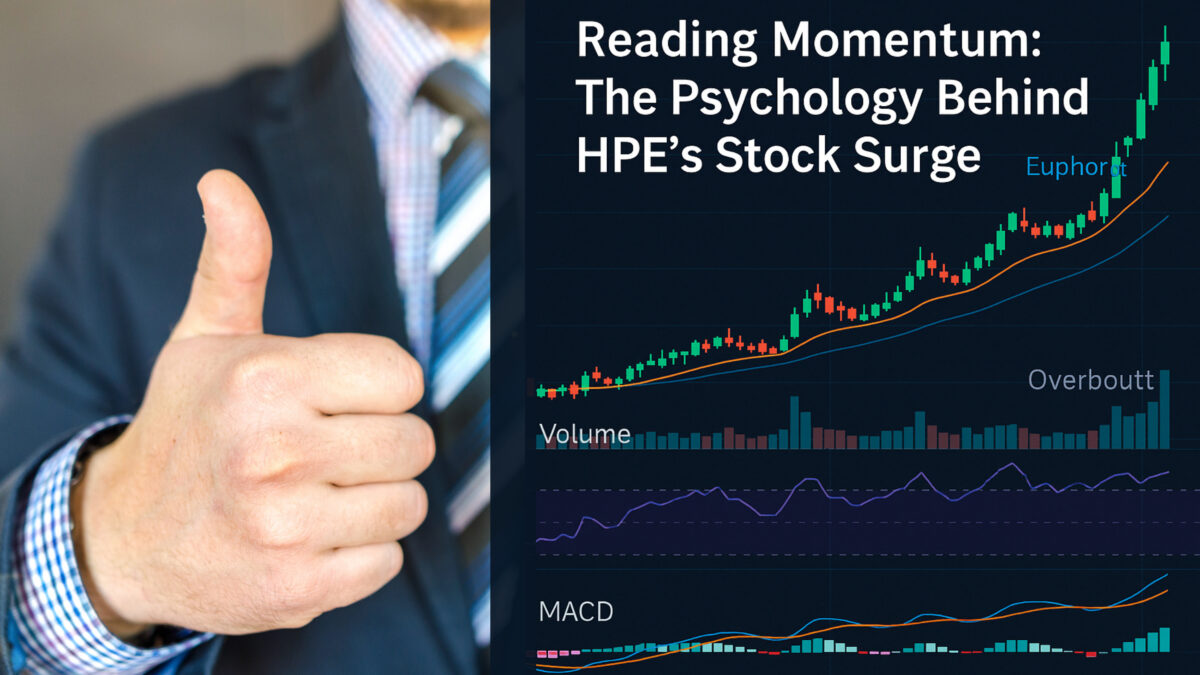
📈 You know that stock’s moment when everyone’s suddenly talking about a stock—and you’re left wondering if you missed the train?
That’s momentum in action. But here’s the thing: by the time most people notice a stock rising, smart investors already saw it coming.
Take HPE, for example. It’s trending now. But the clues were there days (sometimes weeks) before the spike. Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s stock (HPE) has shown notable movement recently — you can view the latest HPE stock data here.
In this post, let’s break down how to read a stock’s momentum—and the hidden signals that most people overlook. Whether you’re an active trader or a casual investor, these insights can help you spot the next opportunity before it hits the headlines.
Table of Contents
📘 Section 1: Introduction — Why Momentum Matters
In the world of investing, momentum is often the most misunderstood force. It’s that invisible current that pushes a stock forward—not necessarily because of solid fundamentals, but because of sentiment, behavior, and smart money making moves early.
We’ve all seen it. A company you’ve never looked at before suddenly starts popping up everywhere—financial news headlines, trending tickers, analyst tweets. Friends are texting you: “Have you heard of this one?” And by the time you check the chart, it’s already up 20%, and you’re left wondering:
Did I just miss my chance?
That’s momentum in action.
But what if you could spot it before the crowd?
What if you could recognize the early signs—subtle volume shifts, unusual buying behavior, or sentiment flips—that hint something big is brewing?
This isn’t wishful thinking. It’s possible.
Let’s take a real-world example: Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE). Over the last few days, its stock has seen a noticeable uptick. The headlines talk about earnings beats or AI infrastructure potential, but if you look closer—investors started making moves before those stories broke. The smart money didn’t wait for the news; it anticipated it.
So how do they do that?
They don’t rely solely on flashy price charts or gut feelings. Instead, they study momentum—not just in terms of price, but across signals like trading volume, sentiment shifts, insider activity, and options flow. Think of it like tuning in to the undercurrent of the market.
In this guide, we’ll decode how momentum really works. We’ll separate the noise from the signal, explore the indicators most investors misuse, and shine light on the lesser-known but powerful clues the pros watch closely.
You’ll walk away knowing:
- What momentum really is (beyond “a stock is going up”)
- Which tools are commonly used—and why they’re not enough
- The hidden signs that often come before a stock moves
- How HPE and other stocks offer teachable moments for smarter investing
Whether you’re managing your own portfolio, trading short-term moves, or simply aiming to sharpen your investment lens—this post is designed to give you a practical, technical, and example-rich blueprint for reading momentum like a pro.
Let’s get started by grounding ourselves in the basics: what exactly is stock momentum, and why is it such a powerful force in modern markets?
📘 Section 2: What is Stock Momentum?
When people say a stock “has momentum,” what they usually mean is: it’s going up and people are buying it fast. But momentum is more than just price movement—it’s the speed and consistency of that movement, often backed by volume, market psychology, and expectation.
In technical terms, momentum is the rate of acceleration of a stock’s price. Think of it like a moving car:
- If the car is going fast and getting faster → strong momentum
- If the car is slowing down → weakening momentum
- If the car changes direction entirely → momentum reversal
📊 Momentum = Price + Time + Volume
Let’s break that down:
- Price: Is the stock rising or falling?
- Time: How quickly is it doing that?
- Volume: Are more people participating in the move?
The formula for basic momentum in technical analysis can be expressed as:
Momentum = Price today – Price N days ago
So if HPE was $15 five days ago and is $18 today, its 5-day momentum is +$3.
But raw price isn’t enough. That’s why traders also use momentum indicators to get clearer signals, which we’ll cover in the next section.
💡 Why Momentum Works
Momentum trading is based on a very human principle: people chase trends.
It starts with a small group of informed investors reacting to a catalyst—say, positive earnings, a product launch, or acquisition rumors. Their early buying pushes the price up. Then, technical traders spot the breakout and join in. Soon, retail investors notice the headlines and pile in, creating a feedback loop of demand.
This “momentum cycle” continues—until it doesn’t.
Understanding when you’re entering the cycle matters. Early momentum gives opportunity. Late momentum carries risk. Recognizing that difference is the key to making momentum work for you, not against you.
📈 Momentum ≠ Hype
One common trap: confusing momentum with hype. A stock trending on social media might seem like it has momentum—but unless it’s backed by:
- Consistent upward price action
- Growing trading volume
- Supporting fundamentals or catalysts
…it may be just noise.
Momentum requires confirmation. It must sustain. Hype can fade in a day. True momentum leaves footprints—on charts, in sentiment, and in trade behavior.
⚡️ Why Investors Should Care
Momentum can act as a:
- Buy signal when supported by volume and trend structure
- Warning signal if a stock is moving too fast without reason
- Confirmation signal when paired with fundamental catalysts (e.g. HPE earnings beat)
Even long-term investors can use momentum to:
- Time entries better
- Avoid buying into dips that turn into crashes
- Ride trend waves while they last
In the next section, we’ll cover the popular but overused momentum indicators—things like moving averages and RSI—and why relying solely on them might lead you into traps.
📘 Section 3: Popular But Overused Momentum Indicators
Momentum traders love indicators. These are mathematical tools that help visualize what price is doing over time—and more importantly, where it might go next.
But there’s a catch: many of these indicators are widely known, so they often end up being reactive, not predictive. If you’re only using these, you’re probably seeing momentum after it’s already begun.
Let’s explore the big three most traders rely on:
🔄 1. Moving Averages (MA50, MA200)
What it is:
A moving average smooths out price data to show trends. The “50-day MA” shows the average closing price of a stock over the last 50 days.
What it tells you:
- Whether a stock is trending up or down over time
- Support/resistance levels
- Trend confirmation (e.g., golden cross = MA50 crossing above MA200)
Why it’s overused:
Everyone sees the same thing. By the time a moving average crossover happens, much of the move has already occurred. It’s great for trend following, but weak for spotting early momentum.
When it’s useful:
- In strong trends, it confirms momentum
- Works best when combined with faster signals (like volume spikes)
⚖️ 2. RSI (Relative Strength Index)
What it is:
RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate whether a stock is overbought or oversold.
Values range from 0 to 100.
- Above 70: overbought
- Below 30: oversold
What it tells you:
- Whether a stock may be due for a correction or bounce
- Short-term momentum exhaustion
Why it’s overused:
RSI doesn’t account for context. A stock can stay “overbought” for weeks during a strong rally. Traders using RSI alone may miss big moves by selling too early.
When it’s useful:
- As a divergence signal (price rising but RSI falling = momentum weakening)
- When paired with volume and trend structure
📊 3. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
What it is:
MACD tracks the relationship between two moving averages (typically 12-day and 26-day) to identify changes in trend strength and direction.
What it tells you:
- Bullish/bearish crossovers
- Trend momentum strength
- Trend reversals
Why it’s overused:
MACD is a lagging indicator—it reacts to price action, not leads it. Many false signals can appear in sideways or choppy markets.
When it’s useful:
- Confirming trends already in motion
- Identifying divergences in longer timeframes
🧠 The Takeaway
These tools aren’t bad—they just need context.
Used alone, they can lead to late entries, false hope, or premature exits. But combined with volume trends, market sentiment, and news flow, they can help paint a more complete picture.
In fact, many experienced traders use these popular indicators as a baseline, then dig deeper with less obvious signals to get ahead of the crowd.
So what are those deeper signals?
📘 Section 4: Hidden or Less-Talked Momentum Signals
While most investors rely on well-known indicators like RSI or MACD, savvy traders dig beneath the surface. They look for subtle cues that reveal early momentum before it becomes obvious on a chart.
Here are some of those hidden signals that can help you read a stock’s momentum like a pro:
🔥 1. Volume-Price Divergence
What it is:
This occurs when price is moving one way and volume is moving the opposite way. For example:
- A stock’s price is rising, but volume is decreasing
- A stock is falling, but volume is increasing
Why it matters:
Volume confirms conviction. If price is rising but no one is participating (low volume), the move is likely weak. But if price is moving and volume is rising, it suggests institutional buying/selling—momentum that matters.
Example:
Suppose HPE rises 5% in 3 days—but volume is half of its usual average. Be cautious—it could be a low-confidence bounce.
Now, if volume triples on a breakout? That’s real momentum.
🧭 2. Relative Strength vs. Sector or Index
What it is:
Compare a stock’s performance not just in isolation, but against its sector or a broader index like the S&P 500.
Why it matters:
If a stock is going up while its entire sector is flat or falling, it’s showing relative strength. That’s a strong momentum cue—money is rotating into that name while others lag.
How to spot it:
Look at charts side by side:
- $HPE vs. $XLK (Tech ETF)
- Or use the Relative Strength (RS) Line if available on your charting tool
🧠 3. Short Interest Changes
What it is:
Short interest measures how many traders are betting a stock will go down. A sudden drop in short interest can signal that shorts are covering (buying back shares)—often ahead of positive momentum.
Why it matters:
Short covering can accelerate momentum, especially when triggered by news, earnings beats, or price breakouts. These can cause “short squeezes.”
Example:
If short interest on a stock drops from 12% to 6% in a week, someone knows something—and the price might reflect it soon.
🔍 4. Options Activity (Unusual Volume)
What it is:
Unusual call buying or put selling often reflects expectations of future price movement.
Why it matters:
Big traders (institutions or insiders) often use options for leverage before taking a large equity position. If you notice a sudden surge in call buying, it can precede a sharp upside move.
Tip:
Sites like Unusual Whales or tools like FlowAlgo can help monitor this. You don’t have to act on every spike, but patterns over a few days are worth noting.
📉 5. Gap Behavior After News
What it is:
When a stock gaps up (or down) after earnings or news, watch what it does next. Does it hold the gap? Continue climbing? Or fade?
Why it matters:
Gaps that hold—especially with volume—often lead to continuation patterns. Gaps that fade quickly signal weak momentum and may reverse.
Pro tip:
A strong earnings gap that holds the opening price for the first hour is often a setup for continued upside.
🧠 Conclusion
Momentum isn’t just about movement—it’s about intent. And these less popular signals can reveal that intent before the charts make it obvious.
When you combine these hidden cues with traditional indicators, you get the complete picture. That’s when you move from guessing… to anticipating.
📘 Section 5: How to Build a Momentum Detection System
By now, you’ve learned about the traditional indicators (RSI, MACD, moving averages) and the hidden signals (volume-price divergence, relative strength, short interest). But how can you combine all this knowledge into a system that gives you a clear view of momentum? Here’s how.
Building a momentum detection system requires:
- Picking the Right Indicators
- Setting up Your Charting and Tools
- Tracking Patterns Over Time
- Interpreting Signals to Make Decisions
Let’s break it down step by step.
1. Picking the Right Indicators
First, select a few key momentum indicators that work best with your strategy. You don’t need everything, just a focused toolkit. Here’s how to choose:
- Short-Term Momentum:
Use RSI (Relative Strength Index) and Volume to gauge if a stock is getting overheated or showing strength in the short term. These are ideal for spotting quick momentum moves. - Trend Confirmation:
Use Moving Averages (like the 50-day and 200-day MA) to confirm whether a stock is in an uptrend or downtrend over a longer period. - Divergence:
Use the RSI Divergence or MACD Divergence to spot when momentum is weakening while the price continues to rise (a classic bearish signal). - Volume Confirmation:
Always check volume. Without volume, price movements lack power. Confirm momentum with an increase in volume.
2. Setting up Your Charting and Tools
Most traders use charting platforms like TradingView or MetaTrader for technical analysis. You’ll want to set up the following:
- Multiple Timeframes:
- Short-term (15-min or 1-hour) for rapid moves
- Medium-term (4-hour or daily) to confirm longer-term trends
- Indicators:
- Add RSI, MACD, and 50-day/ 200-day moving averages to your charts
- Add Volume at the bottom of the chart to gauge strength
- Stock Screening:
Use stock screening tools (like Finviz or TradingView’s screener) to filter for stocks with strong momentum—based on price and volume growth.
3. Tracking Patterns Over Time
Once your system is set up, start monitoring stocks daily. Identify the early signs of momentum before it fully forms. Here’s what to track:
- Watch for Divergence:
When price is climbing and RSI or MACD starts losing steam, that’s a warning. The price could soon reverse. - Volume Surges:
A jump in volume is a red flag for buying pressure or selling pressure—watch closely for new moves. - Trend Breakouts:
Look for stocks breaking out of well-defined price levels (like resistance or support) with volume backing it up. - Compare Sector Strength:
Always compare stocks to their sectors. If a stock is doing well while its sector lags, it’s a sign of relative strength.
4. Interpreting Signals to Make Decisions
Once the signals start showing up, it’s time to interpret them and make a decision. Here’s how you can use them:
- Buying a Stock:
If a stock is showing positive momentum (strong price movement, rising volume, bullish MACD/RSI), consider entering a position once the stock breaks a significant resistance level. Keep an eye on volume for confirmation. - Waiting for Confirmation:
Don’t jump in just yet. Wait for confirmation from other signals. If the price jumps but the volume stays flat, it’s a weak signal. Look for more volume or check if the stock holds above a key level for a few days. - Exit Strategy:
- If the stock is moving upward but RSI goes above 70 or MACD shows a bearish crossover, it’s time to think about exiting.
- If volume starts dropping off and price rises, watch for potential reversals or pullbacks.
🧠 Putting It All Together
By combining multiple indicators, tracking volume, and considering the bigger picture (sector/market context), you can make more informed decisions. Momentum doesn’t lie, but it’s easy to be tricked by false signals if you rely on just one tool.
With practice, you’ll start to see patterns in real-time, which means you can act before the crowd.
Momentum trading isn’t about blind luck. It’s about mastering these signals, fine-tuning your system, and staying disciplined. Once you develop a consistent framework, you’ll be in a much better position to spot momentum shifts early and ride the wave.
📘 Section 6: Risk Management: Protecting Yourself in Momentum Trades
Momentum trading can be incredibly profitable, but it’s important to understand that no trade is ever 100% guaranteed. Even the most solid momentum signals can turn against you. That’s why risk management is a critical element of any successful momentum strategy. The goal is to protect your capital while maximizing potential returns.
Let’s break down how to manage risk when trading momentum stocks:
1. Position Sizing
What it is:
Position sizing refers to how much of your portfolio you’re willing to risk on a single trade. This is your first line of defense against large losses.
How to Use It:
- Rule of Thumb: Don’t risk more than 1-2% of your total portfolio on a single trade.
- Example:
If you have a $10,000 portfolio, risk no more than $100-$200 on any single trade. If the stock moves against you, this ensures you don’t lose too much.
Why it’s important:
Momentum stocks can be volatile, and not every trade will be a winner. By controlling position size, you prevent one bad trade from wiping out a significant portion of your account.
2. Stop Loss Orders: Automatic Protection
What it is:
A stop-loss order is a predefined level at which you decide to exit a losing position. It’s a tool that automatically sells your position when the price hits a certain threshold.
How to Use It:
- Set your stop loss based on technical support levels or percentage risk.
- Support-based stop loss: Place your stop just below key support levels. If the stock breaks below support, it could be a sign that momentum is reversing.
- Percentage stop loss: Set your stop to automatically sell if the stock moves against you by a set percentage (e.g., 3-5%).
Example:
If you buy a stock at $100, you could set a stop loss at $95 (5% below your entry price). If the price falls to $95, the stop-loss order triggers and protects you from further losses.
3. Trailing Stops: Locking In Profits
What it is:
A trailing stop is a dynamic stop loss that adjusts as the price moves in your favor. It helps you lock in profits while still allowing the trade to run as long as momentum continues.
How to Use It:
- A trailing stop is set at a percentage below the current price.
- If the stock rises, the stop adjusts higher, following the price move.
- If the price falls by the set percentage, the stop triggers, locking in your gains.
Example:
- You buy a stock at $100, and it rises to $120.
- You set a 5% trailing stop, which means the stop is now at $114.
- If the stock continues to climb, the trailing stop moves up.
- If the stock then falls back to $114, the position automatically sells, locking in your profit.
Why it matters:
A trailing stop allows you to ride the wave of momentum but automatically protect your profits if the momentum fades.
4. Risk-Reward Ratio: Calculating Profit Potential
What it is:
The risk-reward ratio is a tool that helps you assess whether a trade is worth taking based on its potential risk and reward.
How to Use It:
A standard risk-reward ratio is 1:3, meaning for every $1 you risk, you aim to make $3.
Example:
- If your stop loss is set at 5% below your entry price, and you believe the stock could rise 15%, your risk-reward ratio is 1:3.
- This means that for every $100 you risk, you expect to gain $300 if the stock hits your target price.
Why it’s important:
The risk-reward ratio helps you be objective about whether a trade is worth it. Even if only half of your trades are successful, a solid risk-reward ratio can still lead to profitable outcomes over time.
5. Diversification: Spread the Risk
What it is:
Diversification involves spreading your investments across multiple assets or sectors to reduce the risk of a single poor-performing trade.
How to Use It:
Instead of putting all your capital into one momentum stock, diversify across multiple stocks that show promising momentum. This helps you reduce risk by ensuring that the failure of one trade doesn’t significantly affect your portfolio.
Example:
If you’re trading HPE, don’t just focus on that. Consider adding momentum stocks from different sectors, like tech, healthcare, or energy. By balancing your portfolio, you minimize the risk of a single event (like a poor earnings report) affecting your entire account.
🧠 Conclusion
In momentum trading, risk management isn’t about avoiding losses—it’s about controlling your exposure and protecting yourself when the trade goes wrong. By using tools like position sizing, stop losses, trailing stops, and calculating a risk-reward ratio, you give yourself the best chance of success while still managing risk effectively.
📘 Section 7: Fine-Tuning Your Momentum System: Adapting to Market Changes
(Approx. 500 words)
A momentum system is not a “set it and forget it” tool. The market constantly evolves, and so should your strategy. Fine-tuning is essential for adapting your momentum detection system to changing market conditions and maintaining a consistent edge.
In this section, we’ll explore how to test your system, adjust your strategy, and keep improving your momentum trades for the long haul.
1. Backtesting: Testing Your Strategy with Historical Data
What it is:
Backtesting involves running your momentum system on historical data to see how it would have performed in the past. This allows you to check if your strategy is sound before you risk real money.
How to Use It:
- Use platforms like TradingView or MetaTrader to backtest your system. Most platforms allow you to apply your indicators (RSI, MACD, moving averages, etc.) to historical price data and evaluate trade outcomes.
- Make sure you test over various time periods, including periods of high volatility (crashes, rapid growth) and low volatility (sideways markets).
What to Look For:
- The win rate (percentage of successful trades)
- The average risk-to-reward ratio
- Maximum drawdown (the largest loss from peak to trough)
Why It’s Important:
Backtesting allows you to identify weaknesses in your system and understand its performance over different market conditions. It provides critical insight into what may need adjusting before you risk capital.
2. Paper Trading: Practice Without Risk
What it is:
Paper trading involves placing simulated trades using real market data but without actual money on the line. It’s like practicing in a real-world environment but risk-free.
How to Use It:
- Paper trading platforms are available through brokerages (like ThinkOrSwim by TD Ameritrade) or on charting platforms (like TradingView).
- Set up a practice account and trade according to your momentum strategy. Keep track of your results and compare them to your backtesting findings.
What to Look For:
- How your system handles real-time market conditions
- Whether you’re following your risk management rules consistently
- Psychological factors—whether the pressure of real-time trading affects your decision-making
- For a real-time view of momentum signals, check out HPE’s interactive chart on TradingView.
Why It’s Important:
Paper trading builds your confidence and allows you to practice adapting to the fast-paced changes in the market without risking any real capital.
3. Adjusting to Market Conditions: Fine-Tuning Your System
The market goes through cycles—bull markets, bear markets, and sideways markets. Your momentum system should evolve based on these cycles.
During Bull Markets:
- Focus more on trend-following strategies. Look for breakouts, volume surges, and confirmation from key indicators (like the 50-day MA).
- You may tolerate slightly looser stop losses or larger risk when the market is rising consistently.
During Bear Markets:
- Focus more on short-term momentum and counter-trend strategies.
- Tighten your stop losses and become more risk-averse.
- Use tools like RSI overbought/oversold levels and volume divergence to spot weak stocks likely to drop further.
During Sideways Markets:
- Look for range-bound setups rather than momentum breakouts. Use oscillators like RSI to detect overbought/oversold conditions within the range.
- Avoid chasing large price moves that may not materialize.
How to Adjust:
- Monitor Market Sentiment: Follow news, global trends, and central bank policies. A shift in interest rates, for instance, could signal a transition from bull to bear market.
- Use a Flexible Stop Loss: In volatile conditions, widen your stop loss. In stable markets, keep your stop losses tighter to avoid unnecessary drawdowns.
Why It’s Important:
Understanding the market’s current phase and adjusting your system accordingly maximizes your chances of success. Markets change, and so should your momentum system.
4. Continuous Learning: Stay Updated and Evolve
What it is:
Continuous learning is the process of refining and improving your trading skills over time. Markets don’t stay static, and neither should your strategy.
How to Do It:
- Track performance regularly and review trades. Keep a trading journal to assess what worked and what didn’t.
- Learn from losses: Each losing trade is an opportunity to fine-tune your system. Look for recurring mistakes or areas of improvement.
- Follow financial news and learn from experts. Join trading forums or read expert blogs to stay updated on new strategies and trends.
- Review your indicators periodically. Test new tools or combinations of indicators that may enhance your system.
Why It’s Important:
By staying informed and open to adapting your strategy, you’ll remain ahead of the curve. The market evolves, and your strategy should too.
🧠 Conclusion
Fine-tuning your momentum system isn’t a one-time event—it’s an ongoing process. Through backtesting, paper trading, and regularly adapting to market conditions, you ensure that your system stays flexible and relevant.
With time and experience, you’ll be able to read the market better, adapt faster, and manage risk effectively. Remember, the key to success in momentum trading is consistency. Focus on improving your system, and let the momentum work for you.
📘 Section 8: Mastering Momentum Trading: Advanced Tips & Final Recap
In this guide, we’ve covered the essential elements of momentum trading—from understanding the core principles and identifying momentum stocks to applying risk management and fine-tuning your system over time. Now, it’s time to take everything you’ve learned and elevate your trading game with some advanced tips that will help you master momentum trading.
1. Understand Market Psychology: The Key to Predicting Momentum
What it is:
Market psychology plays a huge role in momentum. Stocks don’t move based on fundamentals alone; they’re also influenced by investor sentiment, fear, greed, and expectations. Being able to read market psychology can give you an edge in identifying momentum before it fully manifests.
How to Apply It:
- Pay attention to news sentiment, especially during earnings season or major geopolitical events.
- Watch for extreme reactions: When stocks rise or fall too quickly, it often signals that momentum may not be sustainable.
- Use social media and forums (like Twitter, Reddit) to gauge the buzz around certain stocks. Strong community sentiment can be an early indicator of growing momentum.
Why It’s Important:
By understanding how emotions affect market behavior, you can get ahead of the curve and spot momentum before it’s obvious to others. Understanding trader psychology is essential — the CFA Institute offers deep insight into how emotions influence market decisions.
2. Combine Momentum with Fundamental Analysis
What it is:
While momentum trading typically focuses on technical indicators, combining it with fundamental analysis can lead to more informed decisions. By examining a company’s financial health, earnings reports, and future growth prospects, you can ensure the momentum is backed by solid fundamentals.
How to Apply It:
- Use momentum indicators to confirm entry points and fundamental analysis to ensure the stock has the potential for long-term growth.
- Focus on growth stocks that show not only price momentum but also signs of strong earnings growth, innovative products, or competitive advantages.
- For example, if a stock is experiencing momentum due to positive earnings reports, verify if the company’s long-term growth prospects justify the move.
Why It’s Important:
Blending technical momentum with fundamental strength can reduce the risk of chasing unsustainable trends. It also provides a more well-rounded approach to trading.
3. Leverage Multiple Time Frames
What it is:
Momentum trading doesn’t just have to happen on one time frame. Using multiple time frames helps you see a broader picture and avoid trading on short-term noise.
How to Apply It:
- Short-term time frames (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts) can be used for entry and exit points.
- Longer-term charts (like 4-hour, daily, or weekly charts) help confirm the overall trend.
- If a stock is showing strong momentum on the 5-minute chart but is in a downtrend on the daily chart, consider waiting for confirmation before entering the trade.
Why It’s Important:
This approach helps you avoid getting caught in false signals or reversals that are typical in short-term fluctuations. By combining short-term momentum with a solid long-term trend, you increase the probability of success.
4. Don’t Overtrade: Patience Is Key
What it is:
One common mistake in momentum trading is overtrading—chasing every opportunity and reacting to every price movement. This can lead to losses and burnout.
How to Apply It:
- Set clear entry and exit criteria for each trade and stick to it. Don’t trade just because you see a stock moving; make sure it fits your strategy.
- Be patient: Wait for strong signals, and be ready to sit out when the market is flat or unpredictable.
- Use a trading journal to track your performance. Analyze which trades were successful and why, and identify the ones where impatience led to mistakes.
Why It’s Important:
Less is more—successful momentum traders know when to stay on the sidelines and only enter when the opportunity is right.
5. Maintain a Strong Psychological Edge
What it is:
The psychological aspect of trading is often the most challenging. Fear of losing or greed to make profits can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive decisions.
How to Apply It:
- Stick to your plan: Develop a clear strategy for both entries and exits and follow it strictly.
- Manage emotions: Use techniques like mindfulness or breathing exercises to stay calm during volatile market conditions.
- Review your mindset: If you’re feeling impatient or stressed, take a step back and reassess your trading approach.
Why It’s Important:
Psychological control is what separates profitable traders from those who burn out. Mastering your emotions and maintaining a long-term perspective is key to sustaining success.
🧠 Conclusion
Momentum trading offers the potential for substantial rewards, but it requires a balance of skill, patience, and discipline. By following a structured approach, incorporating risk management, and fine-tuning your system based on market conditions, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a successful momentum trader.
Remember that trading is a journey, and the more you practice and refine your strategy, the better you’ll become at spotting trends and capturing opportunities. Stay adaptable, keep learning, and focus on consistent improvements—because momentum can be a powerful ally when you know how to ride it.
With that, you’ve now got the tools to master momentum trading. Best of luck, and may your trades be profitable!
Stay Ahead in the Market! 🚀
Want to keep your momentum trading game strong? Subscribe to our newsletter for exclusive insights, market trends, and expert tips delivered straight to your inbox. Don’t miss out on the latest updates that could shape your trading success!
👉 Subscribe Now and get actionable strategies today!
Plus, share this article with fellow traders and help them unlock the secrets to mastering momentum. Let’s grow together!
Disclaimer: The insights and information shared in this article are intended solely for educational purposes and should not be considered as financial or investment advice. Trading or investing in stocks involves risk, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Always do your own research or consult a licensed financial advisor before making investment decisions.